What is SaaS Platform: Everything You Need to Know
Looking for a comprehensive guide about what is SaaS platform? You’ve landed in the right place. Today, in this blog, we will easily describe everything about the SaaS platforms.
Nowadays, SaaS is growing faster than you can think. Everyone around you is either a SaaS builder or a SaaS user. If you don’t believe us, you can ask anyone from your surroundings (fingers crossed).
So, if you want to build a SaaS for your business, or want to explore this trendy topic, you are welcome. We are going to take you on a ride of SaaS where we will discuss literally everything and anything about SaaS platforms.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started!
What is SaaS Platform?
SaaS, short for Software as a Service, is a modern approach to software distribution. In simple terms, it means software applications are hosted by a cloud provider and accessed by users over the internet.
Imagine accessing your favorite apps like Google Docs or Salesforce directly through your web browser without needing to download or install anything on your computer. That’s the magic of SaaS!
For instance, think of Google Workspace (formerly G Suite). Instead of purchasing and installing productivity software like email, document editing, and file storage individually, users subscribe to Google Workspace and access these tools online. It’s convenient, cost-effective, and always up-to-date!
As technology continues to evolve, experts predict the SaaS market will soar to nearly $200 billion by 2024
According to McKinsey & Company report.
This growth highlights the increasing reliance on cloud-based solutions for efficient and scalable software delivery.
Find out more on –
7 Best Tips on How to Build a SaaS Product
How Does SaaS Work?

SaaS, or Software as a Service, operates seamlessly through the cloud delivery model, offering a hassle-free solution for accessing software applications. Discover the inner workings of SaaS with this step-by-step breakdown:
Step 1: Cloud Hosting
SaaS operates via cloud hosting, where a software provider manages the application and its data using their own servers, databases, and computing resources. Alternatively, an Independent Software Vendor (ISV) might enlist a cloud provider to host the application in their data center.
Step 2: Accessible Anywhere
Once hosted, the application becomes accessible from any device with an internet connection. Users can conveniently access it through web browsers, eliminating the need for complex installations or downloads.
Step 3: No Setup or Maintenance
One of the main perks of SaaS is that companies using these applications don’t have to worry about setting up or maintaining the software. Users simply subscribe to the service, paying a subscription fee for instant access to a fully functional solution.
Step 4: Continuous Updates
SaaS providers regularly update their applications with new features and functionalities. Since the software is hosted centrally, updates are seamlessly rolled out to all users without any hassle.
Step 5: Data Management
Depending on the service-level agreement (SLA), customer data can be stored locally, in the cloud, or both. This flexibility ensures data security and compliance with regulations.
Step 6: Integration Capabilities
SaaS applications can be integrated with other software tools using Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). This allows organizations to tailor their software ecosystem to their specific needs, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
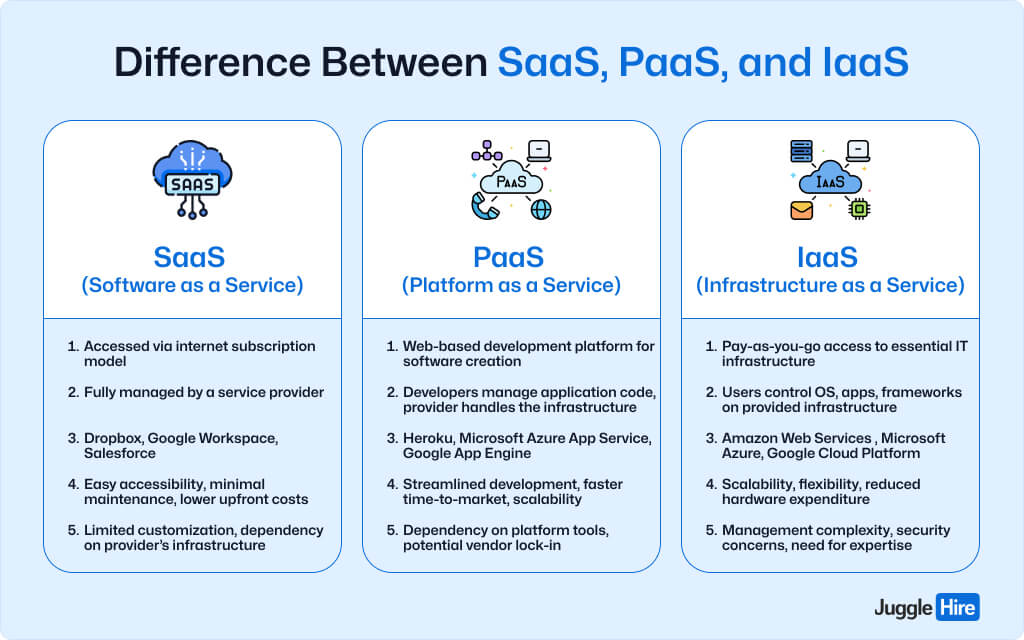
Difference Between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
SaaS delivers ready-to-use software, PaaS empowers developers, and IaaS provides the building blocks for your IT infrastructure. Each serves a unique purpose, catering to different needs in the digital landscape.
Starting with SaaS, or Software as a Service. Picture it as your go-to streaming service, but for software. It’s all about accessing applications online, managed by a third party. Examples include Dropbox, Google Workspace, and Salesforce.
Now onto PaaS, or Platform as a Service. This is like a virtual playground for developers. It offers them a web-based platform to craft software without fretting over storage or infrastructure. Developers can unleash their creativity without getting bogged down in the technical details.
Lastly, there’s IaaS or Infrastructure as a Service. Think of it as leasing the backbone of your IT setup. You gain access to servers, storage, and memory on demand. Need more computing power? Just scale it up. Major players include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Rackspace.
Here’s a simple demonstration of how SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are different:
The Major Types of SaaS
Discover the diverse world of SaaS applications tailored to meet various industry needs. Here are the major types of SaaS software:
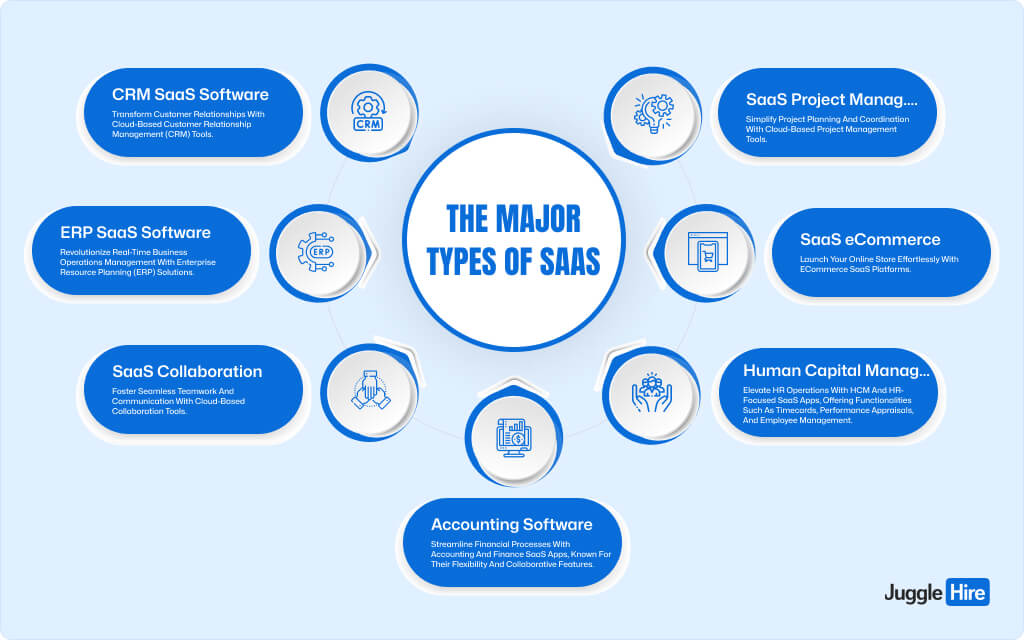
1) CRM SaaS Software
Transform customer relationships with cloud-based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools. These platforms empower businesses to streamline sales processes, enhance marketing efforts, and elevate customer experiences.
Examples –
Leading names include Salesforce, Zendesk, Zoho, and Hubspot.
2) ERP SaaS Software
Revolutionize real-time business operations management with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions. These cloud-based platforms facilitate the financial planning, procurement, project management, and inventory management.
Examples –
Popular choices encompass SAP, Oracle NetSuite, and Microsoft Dynamics.
3) SaaS Collaboration Software
Foster seamless teamwork and communication with cloud-based collaboration tools. These platforms facilitate brainstorming, task organization, and progress tracking.
Examples –
Notable options include Slack, Confluence, and Figma.
4) Accounting Software
Streamline financial processes with accounting and finance SaaS apps, known for their flexibility and collaborative features. These tools empower organizations to manage budgets, track expenses, and enhance financial transparency.
Examples –
Streamline financial processes with accounting and finance SaaS apps like QuickBooks Online, Xero, and FreshBooks.
5) Human Capital Management (HCM) and Human Resources (HR)
Elevate HR operations with HCM and HR-focused SaaS apps. They offer functionalities such as timecards, performance appraisals, and employee management. These tools streamline HR processes, ensuring efficient workforce management and compliance with regulations.
Examples –
Workday, BambooHR, and ADP Workforce Now are some popular mentions.
6) SaaS eCommerce Platforms
Launch your online store effortlessly with eCommerce SaaS platforms. These solutions offer customizable storefronts, payment gateway integrations, and premium features without the need for extensive web development.
Examples –
Key players include Shopify, Bigcommerce, and Volusion.
7) SaaS Project Management Software
Simplify project planning and coordination with cloud-based project management tools. These platforms enable effective task allocation, scheduling, and collaboration among team members.
Examples –
Top choices consist of Jira, Trello, and Basecamp.
Benefits of Using a SaaS Platform

Explore the myriad benefits of Software as a Service (SaaS), offering cost-effective and flexible solutions for diverse business requirements. Let’s delve into the crucial advantages of SaaS.
Test Before You Invest
SaaS providers often offer free trials, allowing you to test their software before committing. This minimizes the risk of investing in tools that may not suit your business needs, leading to better decision-making and resource allocation.
Easy Setup and Accessibility
Access essential tools and data from anywhere with internet access. SaaS platforms are simple to set up and require minimal technical expertise, enabling quick adoption and boosting productivity, whether you’re in the office or working remotely.
Optimized Cash Flow
SaaS subscription models offer predictable, recurring revenue streams for providers while helping businesses manage expenses effectively. This stability enhances financial planning and instills investor confidence, with subscription-based revenue models resulting in higher profit margins and eliminating the need for large upfront investments.
Boosted User Engagement
SaaS platforms foster collaboration and engagement among users, driving productivity and innovation within your team. Real-time communication and remote accessibility promote seamless collaboration, leading to enhanced productivity and team cohesion.
Robust Data Security
SaaS providers prioritize data security, employing encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular updates to safeguard sensitive information. With a focus on data protection, small businesses can rest assured that their confidential data is secure and compliant with regulations.
Cost Reduction
SaaS significantly lowers upfront costs associated with traditional on-premise software. By adopting a pay-as-you-go model, businesses can manage expenses more effectively and mitigate financial risks. Furthermore, SaaS providers handle installation, configuration, and maintenance, eliminating the need for hiring IT professionals and making high-quality software more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Flexible Payment Plans
SaaS models offer flexible payment options, allowing businesses to scale subscriptions based on their needs. With the ability to easily adjust plans, businesses can optimize expenses and ensure they only pay for what they use.
User-Friendly Interface
SaaS products are renowned for their ease of use, eliminating the need for IT expertise or technical support. With up-to-date applications accessible via the internet, employees can quickly adopt new software and focus on core tasks, saving valuable time and resources.
Accessibility and Scalability
Enjoy unparalleled flexibility with SaaS platforms, enabling seamless access and scalability. Hosted externally, SaaS software can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, ideal for remote work and multi-site operations, enhancing productivity and collaboration across teams.
Continuous Updates
SaaS providers continuously update software, ensuring it remains relevant and competitive. Regular updates address bug fixes, introduce new features, and adapt to evolving user needs, benefiting both providers and customers. Clients can effortlessly upgrade to the latest versions, accessing improvements as soon as they’re available.
You should also read –
Benefits of SaaS for Small Businesses
The Downside of Using a SaaS Platform
While Software as a Service (SaaS) brings numerous benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges and risks. Here’s what you need to know:
Reliance on Outside Vendors
Businesses depend on external vendors to provide, maintain, and secure the software. Any disruptions, changes, or security breaches on the vendor’s end can impact the business’s operations and data security.
Loss of Control Over Versioning
SaaS providers may automatically update software versions for all users, regardless of their preferences. This can require additional time and resources for training, as businesses may need to adapt to new features or interfaces.
Difficulty in Vendor Switching
Switching SaaS vendors can be complex and labor-intensive, especially when migrating large volumes of data. Proprietary technologies and data types used by vendors can further complicate the transfer process, leading to vendor lock-in.
Cloud Security Concerns
Security remains a significant challenge for SaaS applications. Businesses must trust their vendor’s security measures to protect sensitive data, but breaches and vulnerabilities in cloud environments are not uncommon.
Popular Types of SaaS Business Models
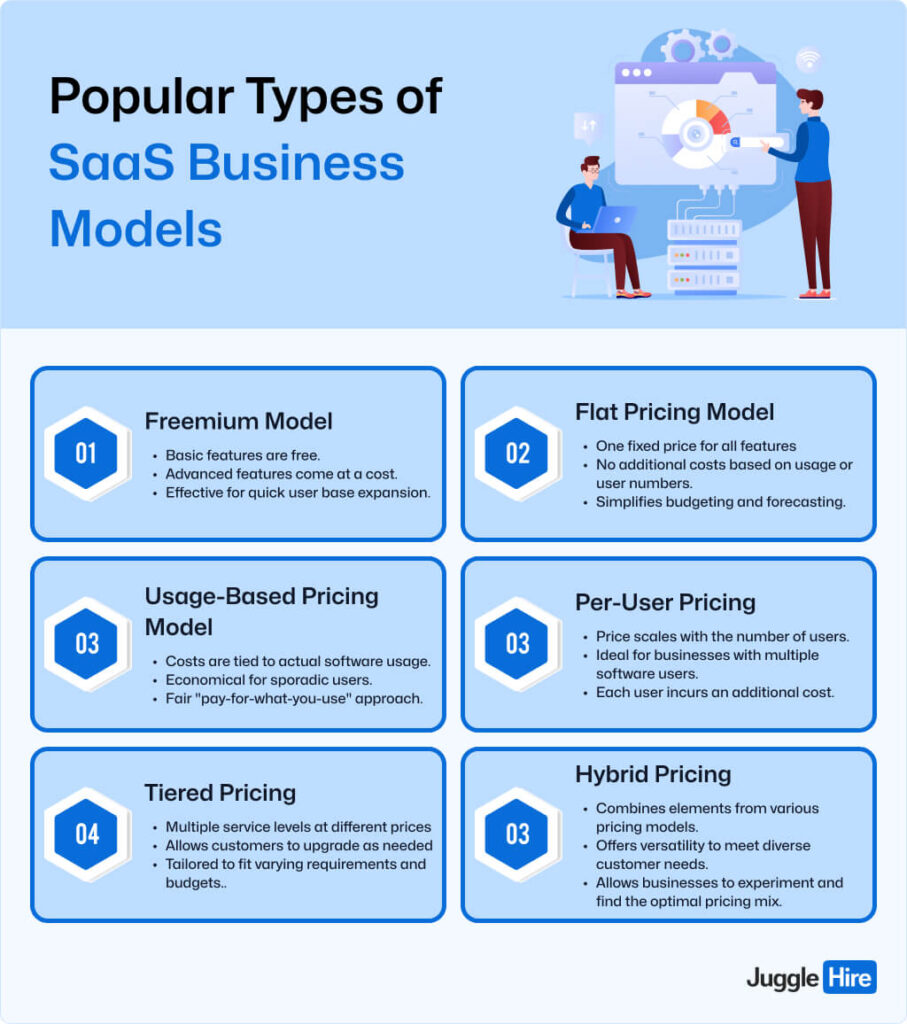
Discover the various types of Software as a Service (SaaS) business models tailored to different user needs:
Freemium Model
The Freemium model offers users a basic version of the software for free, with the option to upgrade to a premium version for enhanced features. This approach enables companies to rapidly expand their user base, banking on the likelihood that some users will opt for the paid version.
Example:
Spotify provides free music streaming with ads. Users can upgrade to Spotify Premium for an ad-free experience and additional features.
Key Points:
- Basic features are free.
- Advanced features come at a cost.
- Effective for quick user base expansion.
Flat Pricing Model
In the Flat Pricing model, users pay a fixed fee for the software, regardless of usage frequency or the number of users. This offers simplicity and predictability, making it attractive to businesses or individuals with fixed budgets.
Example:
Adobe Acrobat Pro DC offers a flat monthly or yearly subscription fee for access to all features.
Key Points:
- One fixed price for all features.
- No additional costs based on usage or user numbers.
- Simplifies budgeting and forecasting.
Usage-Based Pricing Model
The Usage-Based Pricing model bills users based on their actual software usage, measured by data consumption, time spent, or features accessed. This flexible model is economical for infrequent users and is perceived as fair since users only pay for what they use.
Example:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) charges for cloud services based on data storage or computing resources consumed.
Key Points:
- Costs are tied to actual software usage.
- Economical for sporadic users.
- Fair “pay-for-what-you-use” approach.
Per-User Pricing
In this model, the cost is based on the number of individual users or licenses. Commonly used in B2B SaaS solutions, businesses pay per active user, making it transparent and predictable for budgeting.
Example:
Slack charges businesses per active user per month.
Key Points:
- Price scales with the number of users.
- Ideal for businesses with multiple software users.
- Each user incurs an additional cost.
Tiered Pricing
With Tiered Pricing, software offerings are divided into different levels or tiers, each with its own features and prices. Customers can choose a package that suits their needs and budget, catering to a diverse range of users.
Example:
Mailchimp offers tiers such as Free, Essentials, Standard, and Premium, each with varying features and prices.
Key Points:
- Multiple service levels at different prices.
- Allows customers to upgrade as needed.
- Tailored to fit varying requirements and budgets.
Hybrid Pricing
Hybrid Pricing combines elements from multiple pricing strategies, offering flexibility to cater to specific markets or customer segments. By blending different models, businesses can optimize revenue streams and cater to a broader audience.
Example:
Dropbox offers a freemium model with basic storage for free, while users can pay for additional storage or business-specific features.
Key Points:
- Combines elements from various pricing models.
- Offers versatility to meet diverse customer needs.
- Allows businesses to experiment and find the optimal pricing mix.
Security of a SaaS Platform
When it comes to cybersecurity, Software as a Service (SaaS) stands out as a more secure platform compared to traditional software. Unlike traditional software, where the user shoulders much of the security responsibility, SaaS shifts this burden to the independent software vendor and third-party cloud provider.
SaaS offers enhanced security features and measures, including –
- Encryption and key management
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Security monitoring
- Incident response
- Poor integration into broader, company-specific security environments
- Fulfillment of data residency requirements
- Data privacy
- Cost of investing in third-party tools to offset the SaaS security risk
- Lack of communication with technical and security experts during the sales process
These built-in security protocols help mitigate common concerns such as misconfiguration and software supply chain vulnerabilities.
Additionally, SaaS platforms undergo rigorous security checks and compliance audits to ensure they meet industry standards and regulations. This proactive approach to security minimizes the risk of data breaches and ensures data privacy for users.
With SaaS, businesses can benefit from a more secure environment without the need for extensive investments in third-party security tools.
You might be interested in reading –
Top Recruiting Software to Streamline Your Hiring Process
Tips to Use a SaaS Solution

Unlock the full potential of your SaaS solution with the following actionable strategies.
Identify Your Business Needs and Goals
Before diving into selecting a SaaS solution, take time to understand your business requirements and objectives. Analyze your current processes, challenges, and areas needing improvement. Define the specific features and functionalities you need in a SaaS application, considering factors like scalability and security. This clarity will guide you in choosing the right solution aligned with your goals.
Conduct Thorough Research and Evaluation
The SaaS market offers a plethora of options, so research is key. Explore various providers, considering factors like reputation, customer reviews, and pricing models. Request demos or trials to test usability and compatibility with your systems. Making an informed decision ensures you choose a SaaS solution that fits seamlessly into your business ecosystem.
Ensure Data Security and Privacy
Protecting your data is paramount. Prioritize SaaS vendors with robust security measures like data encryption and access controls. Check for compliance with industry standards like GDPR or HIPAA if applicable. Trustworthy vendors with a solid security track record will safeguard your sensitive information effectively.
Plan for Integration and Compatibility
Smooth integration is essential for seamless operations. Assess whether the SaaS solution can integrate with your existing tools and systems. Look for APIs or pre-built integrations that facilitate data exchange. Compatibility ensures your employees can leverage the solution without disruption, maintaining data consistency and accuracy.
Establish a Change Management Strategy
Introducing a SaaS solution means changes in workflows, which can meet resistance. To navigate this, create a change management strategy. Highlight the benefits of the solution to employees, emphasizing how it streamlines tasks and boosts productivity. Provide thorough training and resources to ensure everyone is on board. Address concerns promptly to smooth the transition.
Prioritize User Adoption and Training
User adoption is key to SaaS success. Offer comprehensive training through workshops, webinars, or one-on-one sessions. Develop user-friendly documentation for easy reference. Encourage the sharing of experiences and best practices among employees to foster continuous learning.
Implement a Data Backup and Recovery Plan
Despite robust security measures, having a data backup plan is crucial. Accidents happen, and backups ensure quick data restoration. Determine the backup frequency and methods aligned with your policies. Regularly test the restoration process and consider cloud storage or off-site backups for added protection.
You must check out –
How to Set Recruitment KPIs
How SaaS is Being Used in Different Industries
We have already seen that the SaaS market crossed $143.7 billion by 2022. We are also noticing that industries worldwide are embracing cloud-based applications to streamline operations. However, the proliferation of SaaS tools has led to challenges like app redundancies and shadow IT.
The findings reveal the following percentage of SaaS being used in different sectors:

Let’s delve into how various sectors leverage SaaS solutions:
Healthcare
The healthcare industry relies on SaaS for electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine platforms, and practice management systems. These tools enhance patient care, streamline administrative tasks, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Finance
In finance, SaaS platforms power online banking, financial analytics, and risk management systems. These solutions enable real-time data analysis, enhance decision-making, and improve customer experiences through personalized services.
Education
Educational institutions leverage SaaS for learning management systems (LMS), student information systems (SIS), and virtual classrooms. These tools facilitate remote learning, collaboration among educators, and personalized instruction for students.
Retail
Retailers utilize SaaS for inventory management, point-of-sale (POS) systems and customer relationship management (CRM) software. These solutions optimize supply chain operations, enhance customer engagement, and support omnichannel retail strategies.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector adopts SaaS for enterprise resource planning (ERP), supply chain management, and product lifecycle management (PLM) software. These tools streamline production processes, improve inventory visibility, and drive operational efficiency.
You might want to read –
6 Expert Tips on Chossing the Right Recruitment Software
Top Examples of Successful SaaS Platforms

SaaS platforms revolutionize business operations, offering efficiency and seamless integration. Here are some standout examples:
HubSpot
HubSpot’s CRM platform offers a comprehensive suite of tools for marketing, sales, content management, and customer service. Hosted on Amazon Web Services (AWS), it exemplifies a successful SaaS company.
Recognized for its excellence, HubSpot’s Marketing hub was named one of G2’s Top 100 Highest Satisfaction Products in 2020.
Slack
Slack dominates the chat tool arena, providing businesses with internal messaging, video conferencing, and productivity bots. Trusted by major brands like Netflix and Uber, Slack’s web-based application ensures easy installation and usage. As for security and performance, they are managed directly by Slack.
Zoom
Zoom has become synonymous with remote meetings, experiencing rapid growth amid the pandemic-induced shift to remote work. Zoom’s cloud-based video conferencing tools facilitate seamless communication across devices. Zoom generated significant revenue for the fiscal year 2023. Hence, it has already reflected another triumph in the SaaS realm.
Square
Square simplifies credit card processing, enabling businesses to accept payments without traditional cash registers. Its software easily integrates with computers or tablets, offering products for commerce, banking, and payroll.
Anticipating 80% annual revenue growth, Square’s innovative solutions revolutionize payment processing.
Atlassian
Atlassian’s suite, including Jira, Confluence, and Trello, enhances software development, project management, and collaboration. With cloud-based and server options, Atlassian promotes transparency, empowering teams with visibility into workflows and projects.
Salesforce
As a pioneering SaaS business, Salesforce has revolutionized sales management since its inception in 1999. It aids businesses in sales team management, prospect processing, and client follow-up. Salesforce exemplifies SaaS success, inspiring countless businesses with its effective solutions.
JuggleHire
JuggleHire is a leading SaaS platform streamlining recruitment processes for businesses of all sizes. It makes efficient team building easier with its comprehensive solutions. It is tailored for various roles, from small business owners to department heads. Overall, JuggleHire simplifies hiring tasks, allowing users to focus on business growth.
Find out more –
Introducing JuggleHire: Best Recruitment Software for Small Businesses
The Future of SaaS Platforms
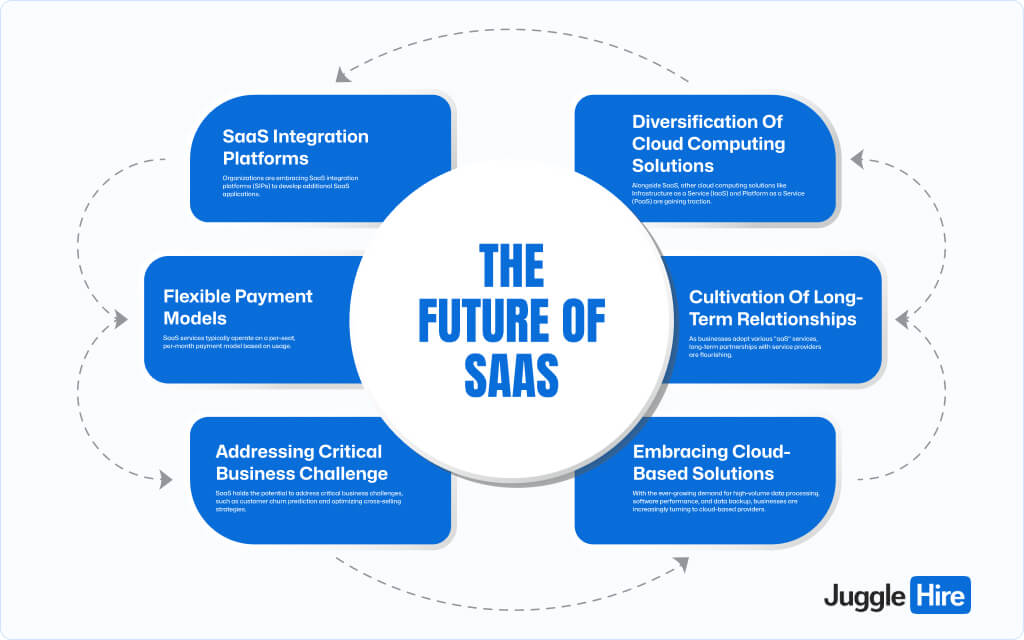
The landscape of Software as a Service (SaaS) is evolving rapidly, reshaping how businesses approach IT solutions. Here’s a glimpse into what lies ahead:
SaaS Integration Platforms (SIPs)
Organizations are embracing SaaS integration platforms (SIPs) to develop additional SaaS applications. These platforms facilitate seamless integration, enabling businesses to build end-to-end solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Diversification of Cloud Computing Solutions
Alongside SaaS, other cloud computing solutions like Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) are gaining traction. The concept of Everything as a Service (XaaS) bundles these solutions together, offering comprehensive IT tools conveniently packaged for businesses.
Flexible Payment Models
SaaS services typically operate on a per-seat, per-month payment model based on usage. This pay-as-you-go approach minimizes upfront costs, allowing businesses to scale resources according to their needs efficiently.
Cultivation of Long-Term Relationships
As businesses adopt various “aaS” services, long-term partnerships with service providers are flourishing. These relationships foster innovation as providers adapt to evolving customer needs, driving continuous improvement and enhanced service offerings.
Addressing Critical Business Challenges
SaaS holds the potential to address critical business challenges, such as customer churn prediction and optimizing cross-selling strategies. By leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities, SaaS platforms may revolutionize decision-making processes and drive business growth.
Embracing Cloud-Based Solutions
With the ever-growing demand for high-volume data processing, software performance, and data backup, businesses are increasingly turning to cloud-based providers. Outsourcing to SaaS platforms offers scalability, reliability, and cost-efficiency, empowering organizations to focus on core competencies while leveraging cutting-edge technology.
Most Common FAQ(s) on SaaS Platform
Which industry is SaaS?
SaaS is a solution utilized across various industries. It’s one of several cloud computing options available for handling business IT needs.
What are the most common uses of SaaS?
Common uses of SaaS include Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Content Management Systems (CMS), Project Management Software, and tools for Sales, Marketing, and e-commerce.
Is SaaS public or private?
SaaS can be both public and private. Public clouds, including SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS services, are hosted on remote servers managed by a provider, and customers access these services over the Internet.
What are the 2 basic components of SaaS?
The two basic components of SaaS are Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems and Marketing automation tools.
We have a series of blog posts on SaaS. You can check them here:
- 10 Reasons to Build a SaaS Application for a New Entrepreneur
- How to Build a SaaS Product – 7 Tips to Turn Your Idea into Reality
- Top 10 Benefits of SaaS for Small Business (+Case Studies)
Everything about SaaS – Ending Note
As we conclude everything about SaaS, it’s clear that this innovative approach to software delivery is reshaping the business landscape. With the evolution of technology trends like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things, SaaS applications are poised to become even more powerful and integrated.
Moreover, the shift towards usage-based pricing models reflects a growing demand for cost-effective solutions. Everything about SaaS is driving efficiency, scalability, and affordability for businesses of all sizes.
