Top 10 Benefits of SaaS for Small Business (+Case Studies)

SaaS or Software as a Service has been adopted by various businesses, whether they are small or large. Recently, we can clearly observe the significant benefits of SaaS for small businesses. Without SaaS, SMEs won’t survive the competition.
By 2023, the worldwide SaaS market hit $333.03 billion, with projections indicating it will soar to $819.23 billion by 2030.
Source: Grand View Research
But what exactly is SaaS in cloud computing, and why should small businesses pay attention? SaaS offers cutting-edge technology within a predetermined budget. It provides complete professional support while optimizing costs and offering unparalleled flexibility.
As a leading SaaS product development company, we’ve curated 10 benefits of SaaS for small businesses, guiding them toward prosperous growth and success.
What is SaaS?
SaaS stands for Software as a Service. Basically, it’s like renting software instead of buying it outright. Instead of installing a program on your computer, SaaS apps live in the cloud. That means you access them through the internet, usually with just a web browser.
Now, here’s the cool part: when you subscribe to a SaaS app, you’re off the hook for all the technical stuff. The heavy lifting of developing and hosting the app? Done for you. It’s like having a personal IT team without actually having to hire one.
The following chart by Statista shows how end users have been spending on SaaS products year after year.
Think about it: with traditional software, you might have to drop serious cash on server hardware and tech wizards to keep everything running smoothly. But with SaaS, all that hassle is handled by the cloud provider. And since you’re just renting the software, you have more flexible payment options. Plus, you can get up and running with a new app in no time.
So there you have it: SaaS is like having your own personal IT genie. It’s convenient, cost-effective, and perfect for businesses big and small.
How Does SaaS Work?
Imagine you’re used to buying CDs to update the software on your computer. It’s a hassle, right? Well, with SaaS, it’s like the software magically updates itself over the internet.
Here’s the deal: SaaS rides on the coattails of cloud computing. Think of the cloud as this big virtual space where all the magic happens – data storage, networking, servers, you name it.
So, instead of buying CDs and downloading updates onto your computer like in the old days, SaaS lets you log in through the internet or your web browser. You connect to the service provider’s network and boom, you’ve got access to the software you need.
Now, who’s hopping on the SaaS train? Well, it’s not just tech companies anymore. Everyone from financial services to entertainment and utilities is jumping on board.
And why should small businesses care? Because SaaS makes life easier. No more wasting time and money on tedious software updates. With SaaS, you can focus on running your business while the software takes care of itself in the cloud. It’s convenient, efficient, and a total game-changer.
Check out –
9 HR Software Implementation Best Practices
How SaaS Model is Different from Traditional Ones?
SaaS (Software as a Service) represents a modern approach to software delivery, where applications are hosted on the cloud and accessed via the Internet. This model differs significantly from traditional software setups, which typically involve installing software on individual devices or servers.
A comparison table will help highlight the key distinctions between SaaS and traditional software in various aspects.
| SaaS (Software as a Service) | Traditional Software | |
| Getting Started | Limited customization options within predefined parameters, prebuilt integrations are available. | You need to install the software on your computer or phone before you can use it. |
| Deployment and Access | Hosted on the cloud, accessed via the internet, no need for installations on individual devices. | Typically installed on each user’s device or a central server, requiring time-consuming installations. |
| Cost Structure | Operates on a subscription basis, with recurring fees for usage. | Involves a significant upfront investment for software licenses, potentially lower ongoing costs. |
| Maintenance and Updates | Service provider handles maintenance, updates, and security patches. | Users are responsible for maintaining and updating the software. |
| Customization and Integration | Data stored on provider’s servers, provider is responsible for security and compliance. | Offers a higher degree of customization, integration requires additional programming or development. |
| Data Security and Compliance | Data stored on provider’s servers, provider responsible for security and compliance. | Users have direct control over data security and compliance measures. |
| Security | It’s more secure, and you don’t need to worry about backing up your data. | It depends on your antivirus software for protection, and you should regularly back up your important data. |
| Users | Many people can use SaaS software at the same time. | Only one person can use traditional software at a time. |
Major Types of SaaS Software
There’s a wide variety of SaaS applications available to meet different business needs. These SaaS solutions offer flexibility, collaboration, and convenience, making them popular choices for businesses of all sizes.
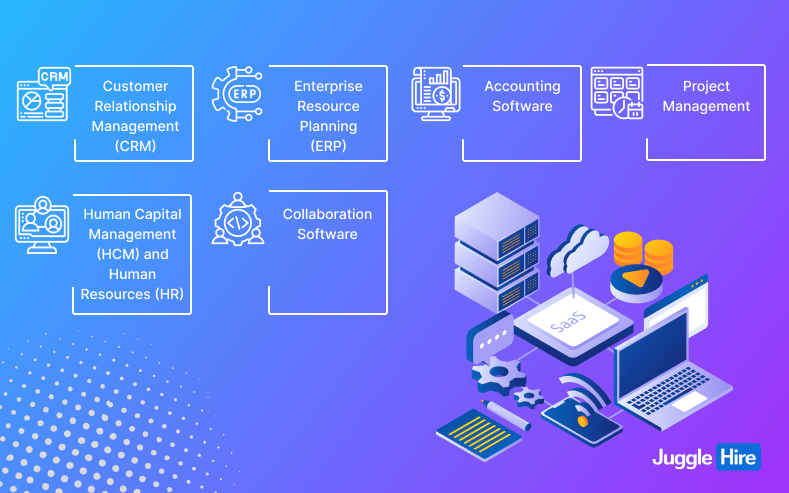
Let’s explore some of the major types:
I) Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM apps are like a one-stop shop for managing customer data and tracking interactions. They’re perfect for sales teams, especially those on the go, as they can access everything they need from anywhere.
II) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP software brings together all the core functions of a business, like accounting, HR, and manufacturing, into one place. It gives businesses a bird’s-eye view of their data, making strategic planning a breeze.
III) Accounting Software
Many organizations love accounting SaaS apps for their flexibility and ability to collaborate on financial matters.
IV) Human Capital Management (HCM) and Human Resources (HR)
HR-focused SaaS apps handle things like timecards, performance reviews, and other HR tasks, making life easier for HR departments.
V) Project Management
SaaS project management apps are a godsend for teams. They make collaborating on projects, allocating resources, and tracking milestones a breeze.
VI) Collaboration Software
Email, calendars, and messaging features now live in SaaS apps, making teamwork smoother than ever.
10 Benefits of SaaS for Small Businesses
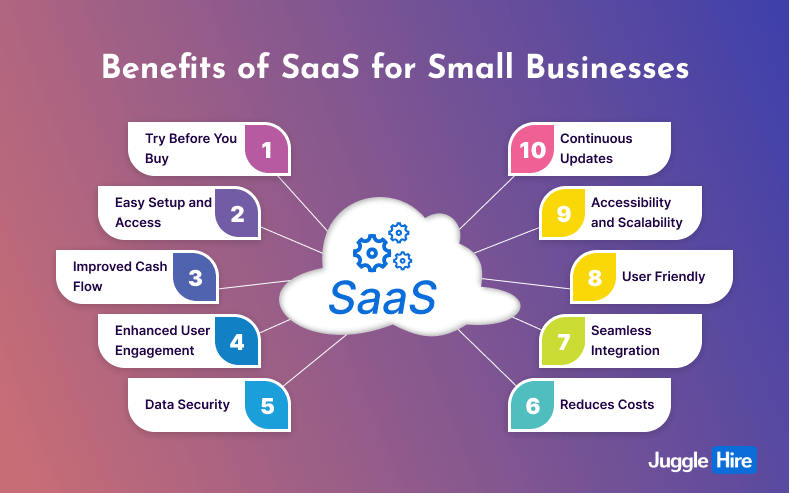
Software as a Service (SaaS) offers a multitude of advantages, providing cost-effective, flexible solutions for various business needs. Let’s explore five key benefits of SaaS for small businesses:
01. Try Before You Buy
SaaS providers often offer free trials, allowing businesses to test their software before making a commitment. This reduces the risk of investing in tools that may not meet the company’s requirements.
Free trials offered by SaaS providers allow small businesses to assess the suitability of software solutions before making a financial commitment. According to a survey by Gartner,
Businesses that offer free trials experience a 30% increase in customer conversions.
This approach reduces the risk of investing in software that may not meet the company’s needs, ultimately leading to better decision-making and resource allocation.
02. Easy Setup and Access
SaaS enables businesses to access essential tools and information from any location with internet access. This accessibility promotes productivity and empowers employees to work efficiently, whether in the office or remotely.
SaaS platforms are typically easy to set up and require minimal technical expertise, allowing small businesses to start using the software quickly. According to a study by Cloud Security Alliance (CSA),
Businesses that adopt cloud-based solutions experience a 20.66% improvement in time-to-market for new products and services.
Additionally, the flexibility of accessing software from any location with internet connectivity enhances employee productivity by enabling remote work opportunities.
03. Improved Cash Flow
SaaS subscription models offer predictable, recurring revenue streams for providers, while allowing businesses to manage expenses more effectively. This stability enhances financial planning and investor confidence.
SaaS subscription models provide businesses with predictable, recurring revenue streams, improving cash flow management. Research by McKinsey & Company indicates that
SaaS businesses with subscription-based revenue models have 9% higher profit margins than those with traditional one-time sales models.
Moreover, the ability to pay for software on a subscription basis eliminates the need for large upfront investments, preserving capital for other business needs.
04. Enhanced User Engagement
Cloud-based SaaS platforms foster collaboration and engagement among users through real-time communication and remote accessibility. This engagement drives productivity and innovation within small business teams.
SaaS platforms facilitate real-time collaboration and communication among users, driving higher levels of engagement. According to a study by Harvard Business Review,
Companies that promote collaborative working environments experience a 15% increase in employee productivity.
What’s more, the accessibility of SaaS tools from multiple devices promotes user adoption and fosters a culture of innovation within small business teams.
Also read –
15 Proven Tips on Building a Strong Employer Brand
05. Data Security
SaaS providers prioritize data security, offering robust measures to protect sensitive information stored on their platforms. This assurance of data safety is crucial for small businesses handling confidential data.
SaaS providers invest heavily in data security measures to protect sensitive information stored on their platforms. According to a report by Cisco,
Organizations that adopt cloud-based security solutions experience a 21% reduction in security breaches.
SaaS platforms employ encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates to safeguard data from cyber threats, providing small businesses with peace of mind regarding data security and compliance.
06. Reduces Costs
SaaS significantly reduces upfront costs associated with purchasing traditional on-premise software. Small and startup businesses may have limited capital. Therefore, they may find it challenging to afford high license fees upfront.
With SaaS, businesses can adopt a pay-as-you-go structure, paying subscription fees over time and based on usage. This subscription-based model lowers financial risk as compared to buying software outright.
Additionally, SaaS providers handle installation, configuration, and maintenance. So, businesses can save expenses of hiring IT professionals. The communal environment of SaaS products means that all customers share the cost of maintenance and updates, making high-quality software more affordable for everyone.
07. Seamless Integration
SaaS models offer flexibility in payment plans, allowing customers to pay for services only when they’re using them. This flexibility enables businesses to adjust their subscriptions based on their needs, whether scaling up or down.
Customers can easily sign up for, cancel, downgrade, or upgrade services as necessary, providing them with control over their expenses and ensuring they only pay for what they use.
08. User Friendly
SaaS products are known for their ease of use, as providers manage IT development, maintenance, and security. Users can access up-to-date applications simply by connecting to the internet and signing in, eliminating the need for IT expertise or technical support.
This accessibility saves time and effort, allowing employees to adopt new software quickly and focus on productive tasks. SaaS vendors handle technical issues and ensure data security. It frees up valuable work hours for clients to focus on core business activities.
09. Accessibility and Scalability
SaaS offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing businesses to change usage plans without advance notice. Since the software is hosted externally by the SaaS provider, it can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making it ideal for remote work and multi-site operations.
Users can access their data and work effectively from any location, enhancing productivity and collaboration across teams.
10. Continuous Updates
SaaS providers are responsible for continuously updating the software. This is how it always remains relevant and competitive. It does the following over time –
- Updates are rolled out regularly
- Addresses bug fixes
- Introduces new features
- Adapts to evolving user needs
This continuous improvement benefits both providers and customers, allowing vendors to refine their products over time and keep customers satisfied. Clients can easily upgrade to the latest versions with a simple click, accessing new features and improvements as soon as they’re available.
You should also read –
Employee Retention Strategies for Small Businesses (Suggested by Professionals)
Success Stories: Businesses Became Successful Using SaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) has emerged as a game-changer for companies seeking scalable, cost-effective solutions. Let’s explore how businesses have leveraged SaaS platforms to drive growth, streamline operations, and achieve remarkable success.
1) Salesforce
Salesforce is a leading cloud-based SaaS company offering a comprehensive software suite for customer service, marketing automation, and application development. Marketers leverage Salesforce to expedite deal processing by tracking customer information and fostering positive customer engagement.
Why Salesforce Stands Out:
With tailored plans for businesses of all sizes and a vast service catalog covering various industries, Salesforce stands out as a versatile solution. It excels not only in sales, customer service, and operations but also in marketing and e-commerce functionalities.
Salesforce Success Story:
Globally, nearly 23% of businesses rely on Salesforce, and the company boasts a workforce in which over 50% are individuals from underrepresented groups.
2) Grammarly
Grammarly sets the standard for AI-powered spellchecking, offering both a Free plan for basic spellchecking and a Plus plan for advanced writing and editing assistance. It provides accurate word and phrase recommendations, identifies poor writing structures like passive voice, and offers verbiage corrections.
Why Grammarly Stands Out:
Grammarly’s robust AI ensures accurate spellchecking and editing, aiding users in crafting polished documents and emails. Moreover, Grammarly’s inclusive approach addresses biases by flagging gendered language and suggesting alternatives.
Grammarly Success Story:
Initially monetized through sales to universities, Grammarly pivoted to the consumer market after garnering substantial revenue. This self-funded venture’s transition to a freemium model was seamless, thanks to its already massive user base.
3) Notion
Notion offers a flexible project management solution distinguished by its block-based system and customizable workspace. It has a user-friendly interface, coupled with drag-and-drop functionality. It allows easy customization of workspace styles, even for non-technical users.
Why Notion Stands Out:
Notion boasts a wide array of features including AI, automation, analytics, tasks, and deadlines, along with seamless integrations like Google Drive.
Notion Success Story:
Despite initial setbacks in 2015, Notion rebounded with increased funding, amassing over 4 million global users and achieving a valuation of $10 billion. Its user-centric approach and adaptable features have contributed to its remarkable success.
You might be interested in –
15 Tips for Managing a Remote Team (with Real Life Stories)
SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS
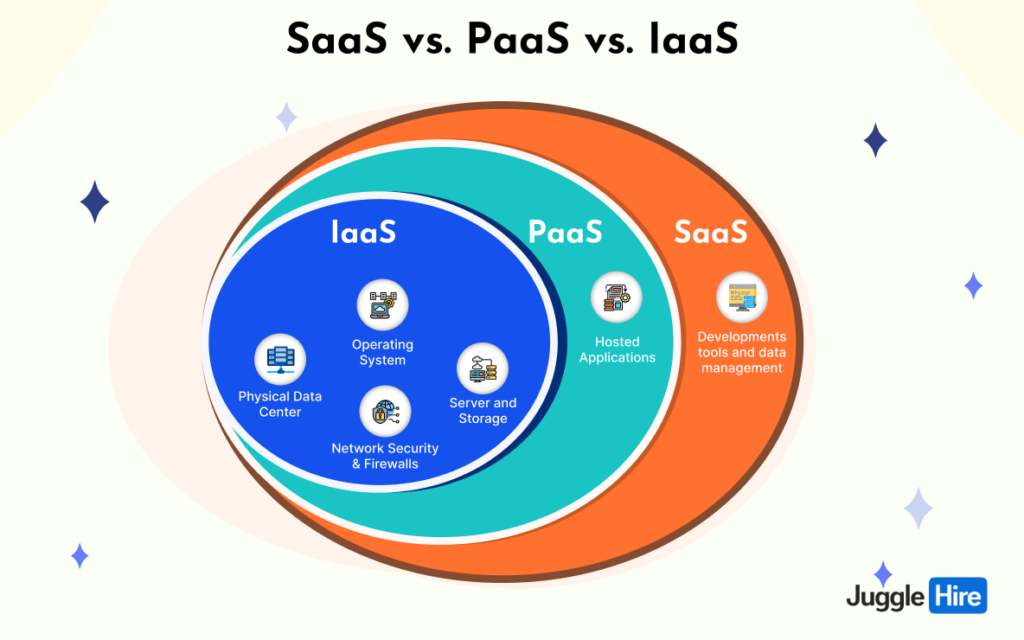
Alright, let’s break down the differences between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS in a nutshell.
First up, we’ve got SaaS, which stands for Software as a Service. This is like your Netflix subscription but for software. You access it over the internet, and a third-party vendor manages all the nitty-gritty stuff. Think Dropbox, Google Workspace, or Salesforce.
Next, there’s PaaS or Platform as a Service. This is like a playground for developers. It gives them a platform over the web to create software without having to worry about storage or infrastructure. They can focus on building cool stuff without sweating the small details.
Last but not least, we’ve got IaaS or Infrastructure as a Service. This is like renting the nuts and bolts of your IT setup. You get access to servers, storage, memory, and more, all on-demand. So, if you need more storage space or computing power, you can just dial it up as needed. Think Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Rackspace.
The following comparison chart highlights the key differences between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS:
| Aspect | SaaS (Software as a Service) | PaaS (Platform as a Service) | IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) |
| Delivery Model | Software applications are accessed over the internet through a subscription model. | Development platform provided over the web, allowing developers to focus on building software. | Access to essential IT infrastructure components such as servers, storage, and networking resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. |
| Management | Managed entirely by the service provider. Users only need to access the software via the internet. | Developers manage the application code, while the service provider handles the underlying infrastructure. | Users have control over the operating systems, applications, and development frameworks, managing them on top of the provided infrastructure. |
| Use Case | Ideal for end-users who require access to software applications without worrying about maintenance or infrastructure. | Best suited for software developers who need a platform to create, test, and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. | Designed for businesses that need scalable computing resources without the upfront costs of purchasing and maintaining hardware. |
| Examples | Dropbox, Google Workspace, Salesforce. | Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Service, Google App Engine. | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP). |
| Benefits | Easy accessibility, minimal maintenance, and lower upfront costs. | Streamlined development processes, faster time-to-market, and scalability. | Scalability, flexibility, and reduced capital expenditure on hardware. |
| Challenges | Limited customization options, dependency on service provider’s infrastructure and updates. | Dependency on specific platform tools and potential vendor lock-in. | Increased management complexity, potential security concerns, and need for expertise in managing infrastructure components. |
Benefits of SaaS for Small Business – Ending Notes
The benefits of SaaS for small businesses are clear and compelling. Features like easy upgrades, lower costs, and enhanced scalability make SaaS the cornerstone of modern computing.
By adopting SaaS solutions, businesses can shed the burdens of complex deployment processes and costly hardware investments, instead of focusing on growth and innovation. As the future of computing continues to evolve towards cloud-based solutions, SaaS stands out as a game-changer for small and medium enterprises.
JuggleHire is an innovative SaaS solution for small businesses. It can eliminate all hiring challenges for SMEs. With the power of JuggleHire, SMEs can propel their growth journey. So, small business owners should embrace the future of business with JuggleHire.
Take the first step today and revolutionize your business with JuggleHire’s SaaS solutions!

Hurray, this is just the right information that I needed. You make me want to learn more!
Glad to hear felix 🙂
Please subscribe to our newsletter for more insightful blogs